Losing a toenail can be an unsettling experience, especially when it happens without any pain. While it might seem alarming, this phenomenon is not uncommon and can result from various causes. This article will explore why toenails sometimes fall off painlessly, the underlying reasons, and how to manage and prevent this issue effectively.
What Is Toenail Loss (Onycholysis)?
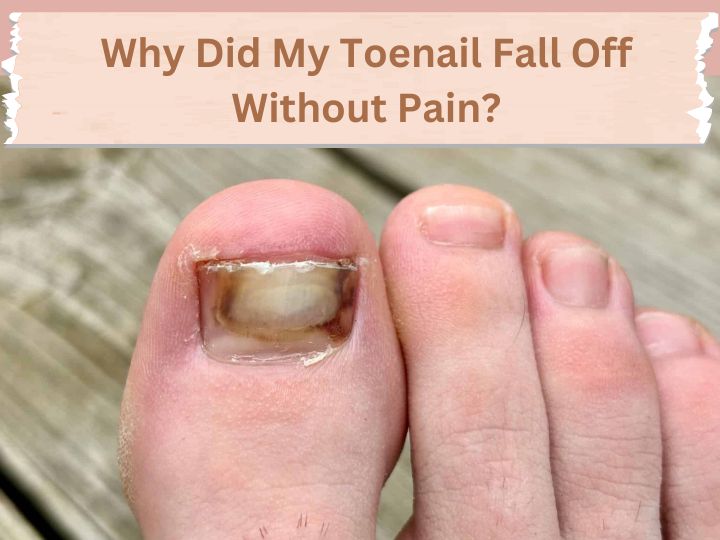
Toenail loss, medically known as onycholysis, occurs when a toenail separates from the nail bed. This separation can happen gradually or suddenly, depending on the cause. In many cases, the absence of pain indicates a slow detachment process, where the nail bed remains relatively unaffected. Understanding the mechanism of onycholysis is crucial to identifying its causes and addressing the condition appropriately.
Common Causes of Painless Toenail Loss
a. Trauma or Injury
Minor trauma or repeated injuries to the toenail can lead to its eventual detachment. For instance, stubbing your toe or dropping a heavy object might not cause immediate pain but can weaken the bond between the nail and the nail bed. Over time, the nail may loosen and fall off without significant discomfort.
b. Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are a common culprit behind toenail loss. These infections weaken the structure of the nail and the underlying nail bed, causing the nail to detach gradually. Symptoms like discoloration, thickening, and brittleness often accompany fungal infections, but they may not always cause pain.
c. Psoriasis or Skin Conditions
Psoriasis, a chronic skin condition, can affect the nails and lead to onycholysis. The buildup of skin cells under the nail can create pressure, causing the nail to lift away from the nail bed. Similarly, other dermatological conditions may contribute to nail detachment without pain.
d. Poor Circulation or Underlying Health Issues
Conditions that impair blood flow, such as diabetes or vascular diseases, can weaken the nails and increase the likelihood of detachment. Poor circulation reduces the delivery of essential nutrients to the nail bed, compromising nail health.
e. Repeated Pressure or Friction
Activities that place repeated pressure or friction on the toenails, such as running or wearing tight footwear, can cause the nails to loosen over time. This is particularly common among athletes or individuals who wear ill-fitting shoes regularly.
f. Chemical Exposure
Harsh chemicals, including some nail polish removers and cleaning agents, can damage the nail structure and lead to detachment. Prolonged exposure to these substances weakens the bond between the nail and the nail bed, resulting in painless loss.
When to Be Concerned
While toenail loss is often benign, certain signs warrant medical attention. These include:
- Discoloration: Yellow, green, or black discoloration may indicate an infection or trauma.
- Foul Odor: A persistent unpleasant smell could signify a fungal or bacterial infection.
- Swelling or Bleeding: Inflammation or bleeding around the nail bed suggests an underlying issue that needs prompt evaluation.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How to Care for a Detached Toenail
a. Immediate Steps After Toenail Loss
When a toenail falls off, taking immediate action can prevent complications:
- Clean the Area: Wash the affected area gently with soap and water to remove dirt and bacteria.
- Bandage the Toe: Cover the exposed nail bed with a sterile bandage to protect it from further injury.
- Avoid Trauma: Keep the area safe from pressure or impact to promote healing.
b. Promoting Healing
To support the healing process:
- Keep the Area Dry: Moisture can encourage fungal or bacterial growth, so ensure the toe stays dry.
- Apply Antiseptics: Use over-the-counter antiseptics to prevent infections.
- Wear Comfortable Footwear: Opt for open-toed or loose-fitting shoes to reduce pressure on the affected toe.
c. Encouraging Nail Regrowth
Nail regrowth can take several months. To support this process:
- Focus on Nutrition: Include biotin, vitamin E, and other essential nutrients in your diet to strengthen nail regrowth.
- Avoid Picking: Refrain from picking at the nail bed or any regrowing nail to prevent further damage.
Preventing Toenail Loss
Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of toenail loss:
- Wear Proper Footwear: Ensure your shoes fit well and provide adequate support to prevent unnecessary pressure on the toenails.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly clean and dry your feet to minimize the risk of infections.
- Trim Nails Properly: Keep your toenails trimmed straight across to prevent them from catching on surfaces or becoming ingrown.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Use gentle, nail-friendly products to protect the nail structure.
Seeking Medical Advice
While many cases of toenail loss can be managed at home, certain situations require professional intervention:
- Persistent Symptoms: If the nail bed shows no signs of healing or remains inflamed, consult a podiatrist.
- Infections: Signs of fungal or bacterial infections, such as discoloration or foul odor, need medical treatment.
- Underlying Conditions: If you suspect a systemic issue like diabetes or poor circulation, seek a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Treatment options may include antifungal medications, topical creams, or in severe cases, surgical intervention.
FAQs
Can a toenail grow back after falling off?
Yes, a toenail typically grows back, but the process can take 6-12 months depending on the individual.
How long does it take for a toenail to regrow?
On average, it takes about 9 months for a toenail to fully regrow.
Is it normal for a toenail to fall off without pain?
Yes, painless toenail loss can occur due to gradual detachment caused by factors like fungal infections or minor trauma.
What are the signs of a fungal infection in toenails?
Common signs include discoloration, thickening, brittleness, and a foul odor.
Should I see a doctor if my toenail falls off?
You should consult a doctor if there are signs of infection, persistent symptoms, or underlying health concerns.
Conclusion
A toenail falling off without pain can be caused by various factors, ranging from minor trauma to underlying health conditions. While the absence of pain is often a reassuring sign, it is essential to identify and address the cause to prevent recurrence and complications. By following proper care techniques and taking preventive measures, you can ensure healthy nail regrowth and overall foot health. If in doubt, consulting a healthcare professional is always a wise choice.