Causes and Risk Factors
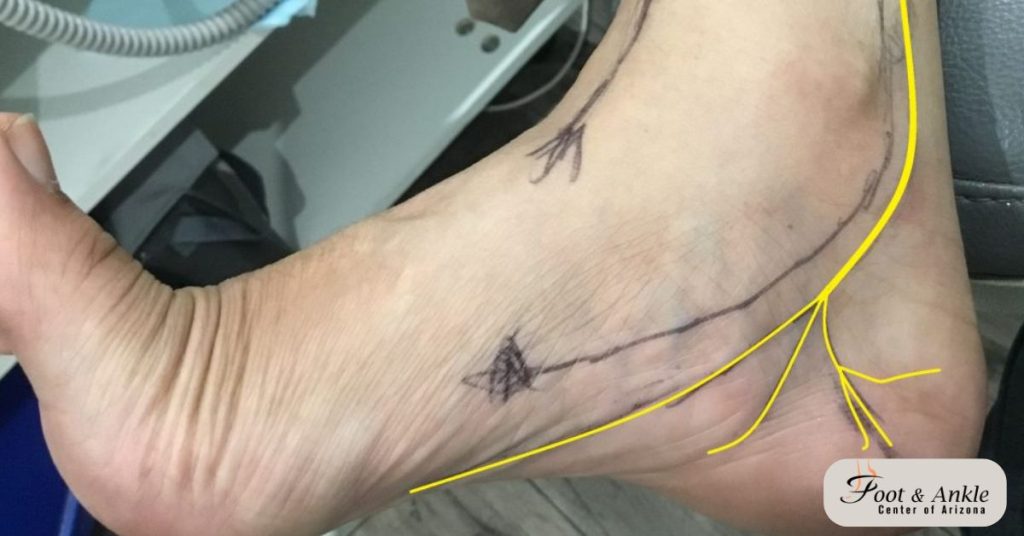
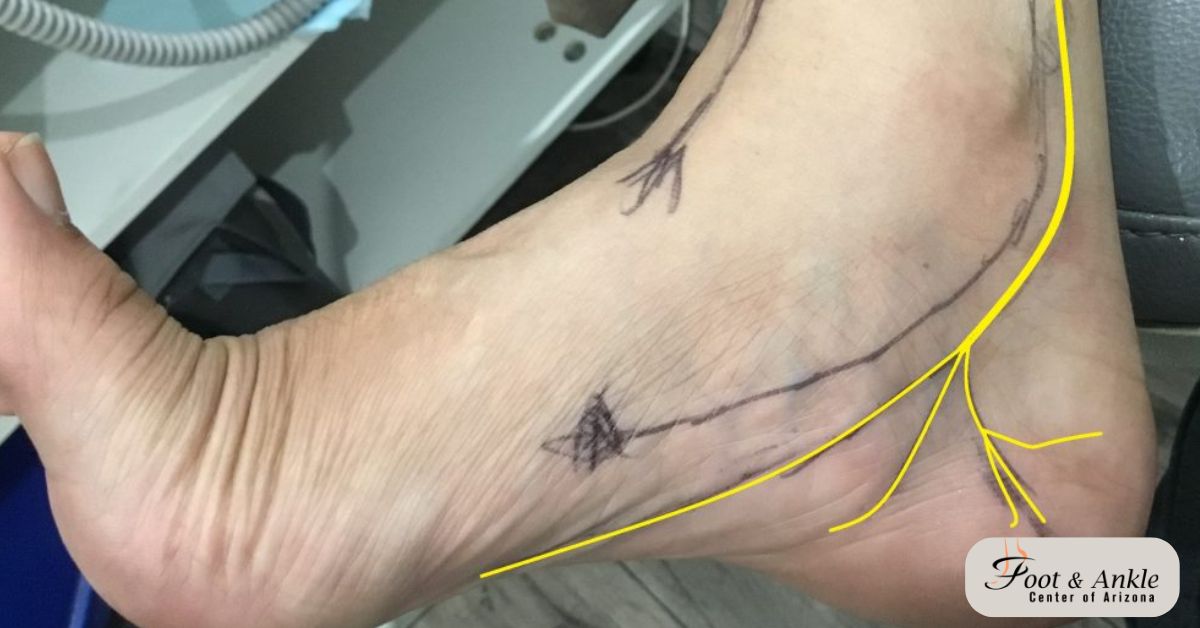
TTS results from the compression of the tibial nerve, which passes through the tarsal tunnel on the inside of the ankle. Next to the ankle lies a narrow passageway formed by bones and ligaments; this is the tarsal tunnel. A tibial nerve and several tendons go through this tunnel. Compression of the tibial nerve can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the foot and ankle.
Causes of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Ankle Injuries: A trauma or injury to the ankle may cause swelling or some structural changes, ultimately compressing the tibial nerve.
- Flat Feet: Those who have a flat foot are most likely to build further pressure on the tarsal tunnel, which consequently causes compression of the nerve.
- Overuse: Cumulative stress or overuse of the foot and ankle, in particular, is seen in athletes, and could be associated with the development of TTS.
- Arthritis: Various diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis, can cause inflammation in the tarsal tunnel and put pressure on the nerve.
- Diabetes: People who have diabetes tend to change nerve functions; this greatly enhances vulnerability to TTS and related disorders.
- Tumors or Cysts: Any kind of growth in or about the tarsal tunnel—ganglion cysts are an excellent example—may put pressure on the tibial nerve.
Risk Factors for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
- Age: With increasing age, degenerative changes in the body occur, which increases the likelihood of TTS.
- Gender: TTS is more common in women than in men, a fact that may relate to both anatomical and hormonal differences.
- Occupation: Those occupations that require standing for a long period and those occupations associated with repetitive movements of the foot increase the risk of TTS.
- Obesity: This carries excess weight around the tarsal tunnel area, thereby compressing the nerves.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome can vary but generally include:
- Pain: Pain in the arch of the foot or anywhere along the course of the tibial nerve, sharp, aching, or throbbing.
- Numbness: A lack of sensation or tingling either in the toes or in the sole of the foot.
- Sensation: These could include burning or stabbing pains running from the ankle towards the toes.
- Weakness: Weakness in the muscles of the foot that causes weakness in gait or balance.
- Swelling: Swelling around the ankle or in the foot may further aggravate the symptoms.
Complications
If left untreated, Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome can lead to several complications, including:
- Chronic pain is when it can prevail for very long periods, impeding the performance of different daily activities and decreasing the quality of life.
- Weakness in the feet: Prolonged pressure on the nerves may cause muscle weakness and thus might affect mobility and gait.
- Atrophy: Nerve malfunction in the foot could result in muscle atrophy of the foot due to reductions in foot strength.
- Secondary Injuries: It can produce compensatory changes in gait, leading to other injuries or additional stress on other parts of the lower extremities.
Getting Medical Help
Medical help should be sought at the first sign of any symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. Tarsal tunnel syndrome can be well treated, and its complications can be prevented if it is diagnosed and treated early. You should see a health professional if:
- Symptoms continue: You are still having pain, numbness, or weakness in your foot or ankle.
- Interference with daily activities: The symptoms interfere with the performance of daily activities or work.
- Worsening Condition: If your condition/symptoms worsen or are not getting better after initial treatments.
- Weakness in Foot: If you are having difficulty walking or an inability to maintain balance due to weakness in the foot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome involves several steps:
- Previous Medical History: The health professional will talk about your previous medical conditions, past injuries, symptoms, and underlying diseases.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam will be done for pain, tingling, or swelling. The doctor may conduct some small tests to provoke the symptoms, such as tapping on the tarsal tunnel (Tinel’s sign) or testing for sensitivity or muscle strength.
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays or even MRI or ultrasound, may be done to visualize the tarsal tunnel better for assessing structural abnormalities and ruling out other conditions.
- Electrodiagnostic Tests: Nerve conduction studies or EMG may be done to evaluate nerve functioning and confirm the TTS diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome aims to relieve symptoms, reduce nerve compression, and address underlying causes. Options include:
Conservative Treatments:
-
- Rest: Activities that provoke the symptom may be avoided or modified to reduce pressure on the tibial nerve.
- Ice Therapy: The application of ice to the affected part decreases inflammation and thus diminishes the pain.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are extremely useful in controlling pain and inflammation.
- Orthotics: Custom-made orthotic inserts support the foot and decrease pressure on the tarsal tunnel.
- Physical Therapy: Such exercises and stretches will decompress nerves, increase flexibility, and provide strength to the foot and ankle area.
Medical Interventions:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief of symptoms.
- Diabetic Management: For individuals with diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels can help manage symptoms and prevent progression.
- Surgical Treatment: If conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary to decompress the tibial nerve. Surgery typically involves releasing the ligament or other structures compressing the nerve.
Outlook
The prognosis for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, broadly speaking, depends upon the acuity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. Most people derive considerable relief from conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and orthotics. Surgery is usually effective in providing long-term relief, although recovery time and outcomes vary.
Prevention
Preventing Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome involves minimizing risk factors and addressing underlying causes:
- Proper Footwear: Wear supportive and well-fitting shoes to reduce pressure on the tarsal tunnel.
- Avoid repetitive stress: If activities require repeated foot movement or place excessive stress on the ankle, they should be modified.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping body weight under control can put less pressure on the tarsal tunnel and reduce the chances of developing TTS.
- Look after Your Feet: Examine your feet regularly and take good care of them to recognize any problems early, and thus avoid complications.
FAQ
What triggers Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome?
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is often triggered by activities or conditions that place excessive pressure on the tibial nerve, such as repetitive ankle movements, flat feet, or injury to the ankle.
What is the fastest way to cure Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome?
The fastest way to alleviate symptoms includes rest, ice therapy, NSAIDs, and orthotic support. For persistent cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be required.
Does Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome ever go away?
Many individuals experience improvement with conservative treatments. Severe cases may require surgery for complete resolution of symptoms.
What happens if Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome goes untreated?
If untreated, Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome can lead to chronic pain, muscle weakness, and difficulty walking, potentially causing long-term functional impairments.
Summary
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition caused by compression of the tibial nerve in the tarsal tunnel of the ankle. It results in pain, numbness, and weakness in the foot. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. Conservative treatments, such as rest, physical therapy, and orthotics, are often successful in relieving symptoms, while surgery may be necessary for severe cases. Adopting preventive measures and addressing risk factors can help reduce the likelihood of developing TTS. If you experience symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, consult a healthcare provider to explore appropriate treatment options and maintain optimal foot health.