What Is Gangrene?
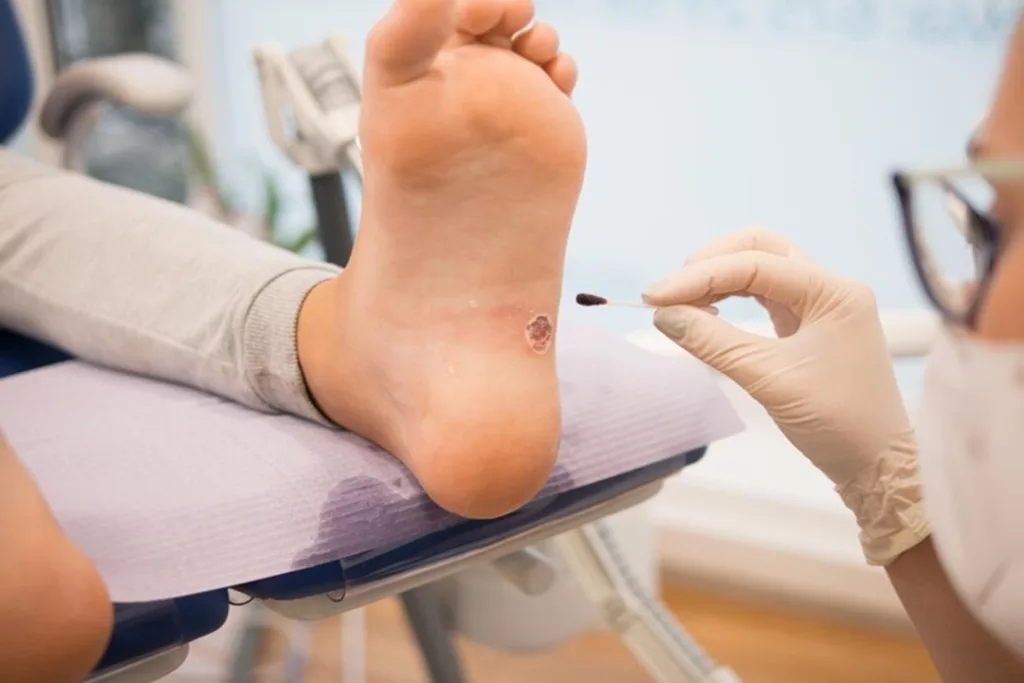
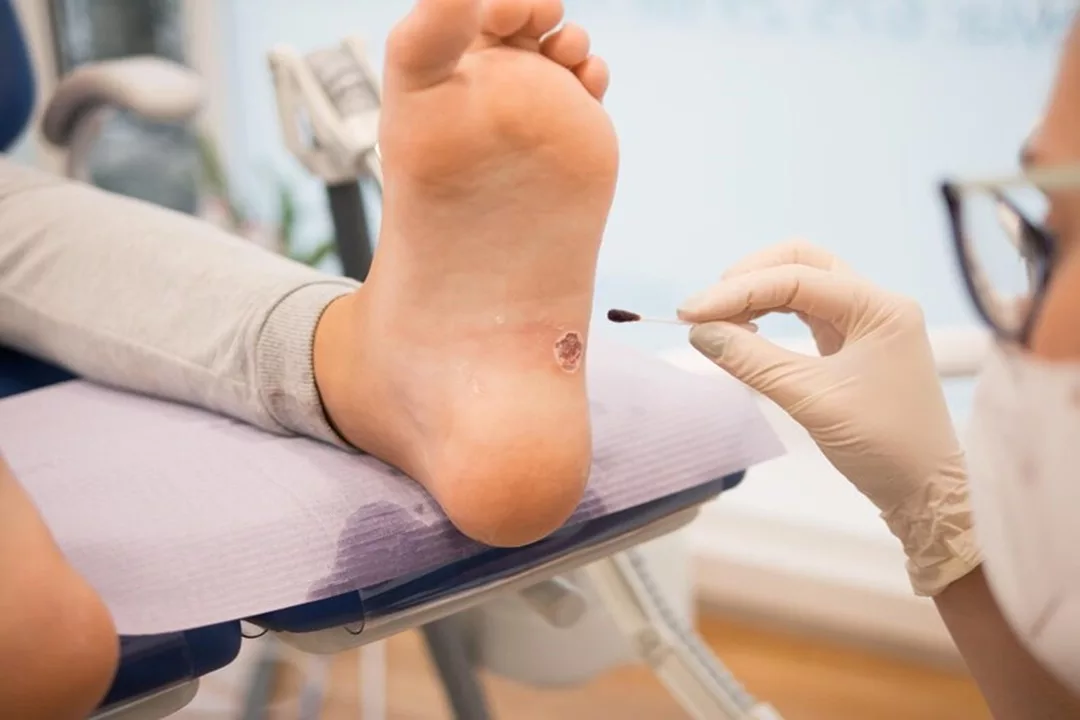
Gangrene is a condition that arises when a particular tissue lacks an adequate blood supply, depriving it of oxygen and leading to the deterioration and decay of the affected tissue. The two primary types of gangrene are wet gangrene, which results from a bacterial infection, and dry gangrene, which occurs without an infection. The risk of developing gangrene is higher for individuals with underlying conditions that can impair blood vessel function and blood flow, such as diabetes or atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Causes of Gangrene
Gangrene most commonly occurs due to conditions like diabetes, arteriosclerosis, tobacco abuse, as well as injuries, burns, and frostbite. The onset of gangrene may stem from a wound or injury that struggles to heal due to insufficient blood supply to the affected area.
Symptoms of Gangrene
The symptoms of gangrene can vary but often include:
- Skin discoloration, ranges from pale to blue, purple, black, bronze, or red, depending on the type of gangrene.
- Swelling
- Blisters
- Sudden, severe pain followed by a sensation of numbness
- A foul-smelling discharge from an affected sore
- Cool or cold skin to the touch
If the disease involves tissues beneath the skin’s surface, as in cases like gas gangrene, it may also be accompanied by a mild fever and a general feeling of unwellness.
Diagnosis of Gangrene
The diagnosis of gangrene typically begins with a physical examination to identify initial changes in the skin. In some cases, additional imaging may be required to rule out conditions like gas gangrene or osteomyelitis.
Non-surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatments for gangrene may involve localized wound care and careful monitoring of the affected area.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Surgical intervention becomes necessary when other treatment options prove ineffective or unsuitable. Treatment typically involves the surgical removal of the dead tissue, which may require partial amputation. Antibiotics are also employed if an infection is present. Additionally, surgical procedures aimed at restoring blood flow are often crucial.
Why Choose a Foot and Ankle Surgeon?
Foot and ankle surgeons are the foremost experts in the field of foot and ankle care. As doctors of podiatric medicine, also referred to as podiatrists (DPMs) or occasionally as “foot and ankle doctors,” they are board-certified surgical specialists specializing in podiatry. Foot and ankle surgeons possess a higher degree of education. And specialized training concerning foot and ankle conditions than any other healthcare providers.
These specialists are equipped to treat a comprehensive range of foot and ankle conditions, from the straightforward to the complex, in patients of all age groups, including cases of the disease. Their rigorous education and training make them qualified to perform a wide spectrum of surgeries, including those that may be necessary for addressing gangrene.