Causes of Significantly Chronic Despair — Chronic Ankle Instability. It usually develops after repeated ankle sprains and can affect both athletes and non-athletes. People suffering from this condition feel that their ankle is unstable or wobbly especially while walking, running, or standing.
Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Ankle Instability
Symptoms of chronic ankle instability may include:
- Breaking the ankle repeatedly, especially on uneven ground or during sports.
- Continued pain and swelling.
- Pain or tenderness near the ankle.
- A sensation of instability or weakness in the ankle joint.
Chronic Ankle Instability Causes
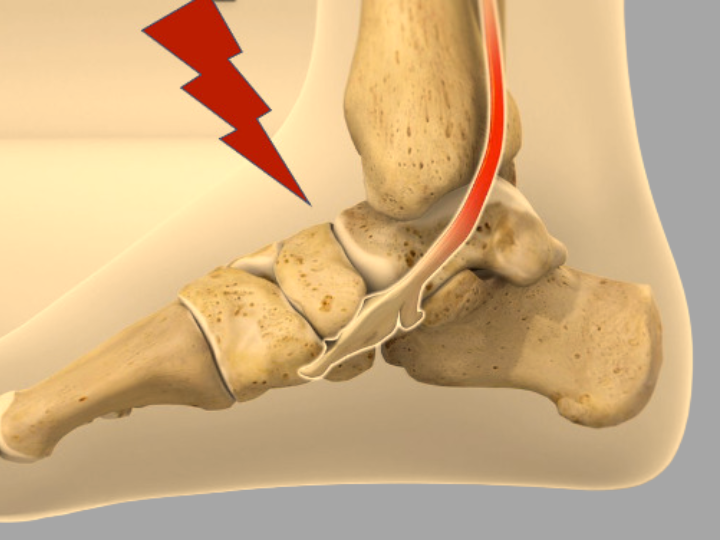
Chronic ankle instability typically develops from an improperly healed or poorly rehabilitated ankle sprain. When the ligaments in the ankle are overextended or properties that were the body’s balance system and the dizziness world. Yet without rehabilitation, these ligaments do not return to their original strength and elasticity, resulting in repeat sprains and increasing instability.
With each repeated ankle sprain (and the sprain that never fully heals), the ligaments become weaker and, as a result, chronic ankle instability becomes a progressively leaching home. Over time, with ongoing instability, this may lead to joint degeneration and other long-term ankle problems.
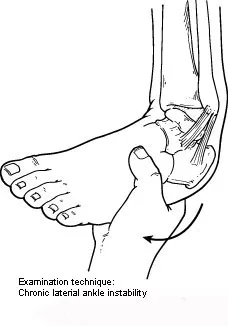
Diagnosis: Chronic Ankle Instability
A foot and ankle surgeon will inquire about the patient’s history of ankle injuries and episodes of instability (ie, chronic ankle instability). In a physical exam, a doctor looks for tenderness, swelling and signs of tearing in the ligaments. Diagnostic imaging tests (e.g., X-rays or MRI scans) may be ordered to assess the extent of ligament damage and exclude other potential conditions.
Conservative Management of CHRONIC ANKLE INSTABILITY
Treatment of chronic ankle instability depends on the grade of the condition and the activity level of the patient. Non-surgical possibilities typically involve:
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises and therapies will assist in enhancing ankle strength, balance, range of motion and muscle coordination. Sport-specific training for athletes is also a common focus of rehabilitation programs.
- Wrap: The wrap is used to give a brace on the ankle which reduces rolling and prevents repeated spraining.
- Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can be used to reduce the pain and swelling.
When Is Surgery Required?
Severe cases can require surgery, especially when non-surgical remedies fail to help. In such cases, a foot and ankle surgeon will determine whether surgical intervention is necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged ligaments. The type of surgical procedure is dependent on the amount of instability and the patient’s overall activity level.
The party will help restore overall function after recovery from surgery (with varying downtime depending on surgical approach).
When to See a Foot and Ankle Surgeon?
Chronic ankle instability — Foot and ankle surgeons are experts at diagnosing and treating conditions such as chronic ankle instability. Podiatrists are extensively trained in the areas of diseases and surgeries of the feet and lower legs and are perfectly equipped to perform such treatment, including ligament reconstruction surgery. Evaluation and management by a foot and ankle surgeon will prevent chronic problems associated with dysfunctional stability mechanisms.
This chronic problem occurs when your ankle joint is so unstable that you risk falling or experiencing pain and decreased mobility.